Bitcoin Price Analysis Using Bollinger Bands: A Strategic Approach
With the rapid evolution of cryptocurrency markets, many traders are left pondering over effective strategies to predict price movements. A significant concern is how to analyze historical price data to guide investment decisions. The use of Bollinger Bands for Bitcoin price analysis using Bollinger Bands (HIBT) has surfaced as a reliable method. This approach not only aids in determining entry and exit points but also helps traders avoid emotional trading decisions.
Understanding Bollinger Bands: A Primer
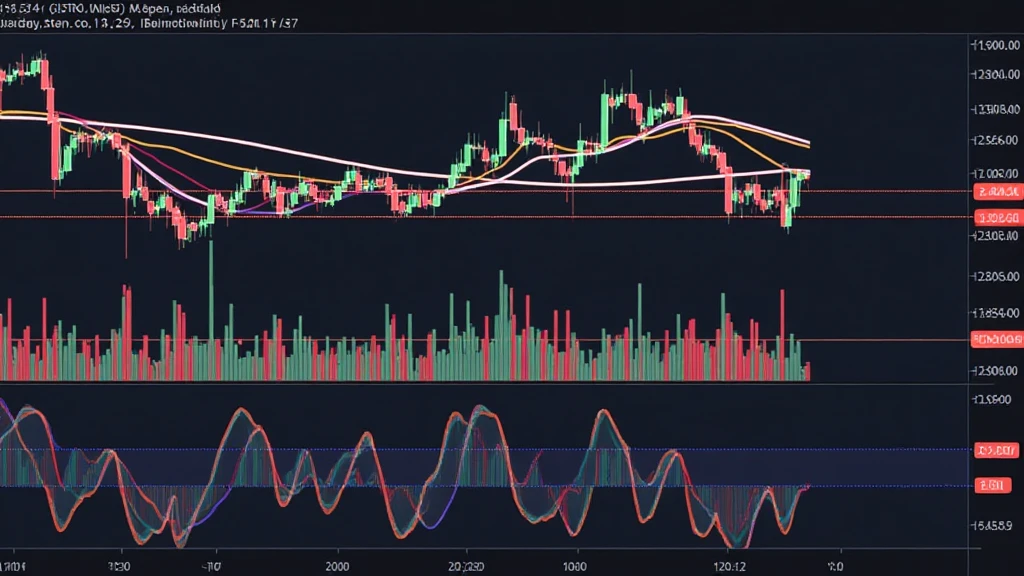
Bollinger Bands, created by John Bollinger in the early 1980s, consist of three lines: a simple moving average (SMA) in the middle and two standard deviation lines (upper and lower) on the sides. These bands provide insights into price volatility and trends. As the bands expand or contract, they signal changes in market conditions, making them a crucial tool for traders.
The Formula Behind Bollinger Bands
The Bollinger Bands can be calculated using the following formula:
- Upper Band = Middle Band + (2 x standard deviation)
- Middle Band = 20-day simple moving average (SMA)
- Lower Band = Middle Band – (2 x standard deviation)
This setup allows traders to gauge whether the price of Bitcoin is relatively high or low based on the standard deviation of the price changes. When Bitcoin prices hit the upper band, it may indicate overbought conditions, while prices at the lower band suggest oversold conditions.
Applying Bollinger Bands to Bitcoin Trading
When it comes to using Bollinger Bands for Bitcoin trading, there are several strategies you can adopt. Here are some effective techniques:
1. Trend Confirmation
When the price consistently moves along the upper or lower bands, it suggests a strong trend. A trader can look for additional confirmations of the trend, potentially entering positions that align with the direction of the price movement.
2. Price Reversals
Conversely, when prices touch the upper or lower bands, it might signal a potential reversal. Traders can watch for bouncing off these bands as a cue to enter trades in the opposite direction. For instance, if Bitcoin bounces off the lower band, it might be an opportunity for buying.
3. Volatility Measurement
Bollinger Bands are also excellent for measuring market volatility. A squeeze, where the bands come close together, indicates low volatility and typically precedes a significant price movement. Traders can prepare for sudden changes during these squeezes.
Analyzing Bitcoin Price Movements in the Vietnamese Market
As Vietnam experiences a surge in cryptocurrency adoption, understanding local trends is vital. With a reported 20% increase in active crypto users in Vietnam in 2024, applying tools like Bollinger Bands becomes even more critical for local traders.
Recent Bitcoin Price Trends in Vietnam
Throughout 2024, Bitcoin has witnessed fluctuations driven by both domestic and global events. Understanding these dynamics through Bollinger Bands can guide traders in making informed decisions:
- In late 2024, a significant dip saw prices reach the lower Bollinger Band, indicating a potential buying opportunity for many investors.
- As the market recovered, a sustained price rise hit the upper band, suggesting traders should be cautious about overextending their positions.
Case Studies: Practical Applications of Bollinger Bands
Studying historical Bitcoin price charts through the Bollinger Bands lens reveals valuable insights into practical applications for traders. Here are notable case studies:
Case Study 1: Late 2024 Market Movements
During a volatile period in November 2024, Bitcoin fluctuated widely. A squeeze in the Bollinger Bands indicated the market was ripe for a breakout. Subsequently, a price surge validated this approach, leading traders who acted promptly to profitable trades.
Case Study 2: Trading Strategies for Novice Traders
New traders often struggle with emotional decision-making. By adhering to Bollinger Bands signals, they can remain disciplined. For instance, a novice trader utilizing the upper and lower bands to set stop-loss orders could avoid unnecessary losses during volatile swings.
Challenges and Limitations of Using Bollinger Bands
Despite their effectiveness, Bollinger Bands are not foolproof. Their major limitations include:
1. False Signals
Market conditions can lead to false breakouts, where prices touch the upper or lower bands without sustaining the trend.
2. Lagging Indicator
As a lagging indicator based on historical data, Bollinger Bands don’t anticipate market changes; they reflect what has already occurred.
Optimizing Your Bitcoin Trading Strategy
Effective use of Bollinger Bands requires combining them with other technical indicators. Here are suggestions to optimize your analysis:
1. Integration with Other Indicators
Coupling Bollinger Bands with indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) provides a comprehensive view of market momentum and trend confirmations.
2. Adapting to Market Conditions
Every market phase requires a different approach. Understanding whether the market is trending or ranging helps traders decide the best Bollinger Bands strategies to adopt.
Conclusion: Enhancing Your Trading with Bollinger Bands
As Bitcoin remains a focal point of the global economy, using Bollinger Bands for price analysis serves as a critical tool for both novice and experienced traders. By staying informed and applying strategic trading methods, you can navigate the market’s complexities.
Remember, the cryptocurrency landscape is often unpredictable. However, with the right tools—like Bollinger Bands—traders can mitigate risks and seize opportunities while ensuring they make evidence-based decisions in their trading strategies.
For further insights and resources on Bitcoin trading strategies, keep up with our latest updates at hibt.com.
Author: Dr. John Smith, a cryptocurrency analyst with a PhD in Finance and over 15 research papers published on market analysis. He has led significant audits of both centralized and decentralized projects in the blockchain sector.



